《数据密集型应用系统设计》第2章-数据模型与查询语言
目录
关系型数据库
以一份简历为例,关系型数据库将其保存为主表和多个表,然后通过外键关联:
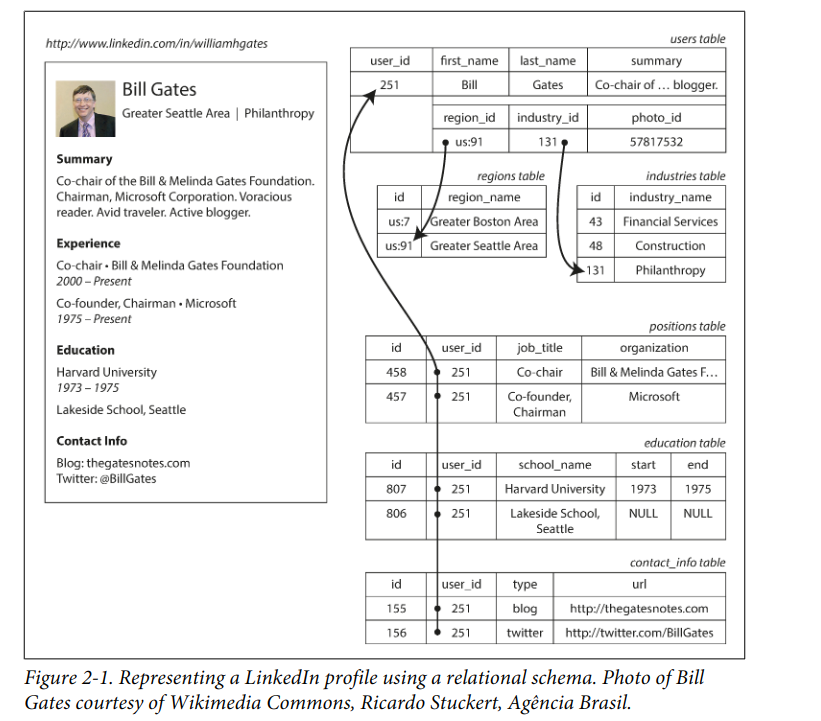
关系型数据库定义了很多种范式,实际这些范式价值并不大。一个经验法是:如果复制了多份重复的数据,则违反了规范化,是不可取的。
文档型数据库
以一份简历为例,文档型数据库将其保存为一个JSON文档:
{
"user_id": 251,
"first_name": "Bill",
"last_name": "Gates",
"summary": "Co-chair of the Bill & Melinda Gates... Active blogger.",
"region_id": "us:91",
"industry_id": 131,
"photo_url": "/p/7/000/253/05b/308dd6e.jpg",
"positions": [{
"job_title": "Co-chair",
"organization": "Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation"
},
{
"job_title": "Co-founder, Chairman",
"organization": "Microsoft"
}
],
"education": [{
"school_name": "Harvard University",
"start": 1973,
"end": 1975
},
{
"school_name": "Lakeside School, Seattle",
"start": null,
"end": null
}
],
"contact_info": {
"blog": "http://thegatesnotes.com",
"twitter": "http://twitter.com/BillGates"
}
}
文档型数据库适用于这种一对多的关系(positions、education),它通常是一次加载整棵树。但是对于多对多的关系支持得不是很好。
图数据库
图数据库通常有两种表示方法或其变体:
属性图
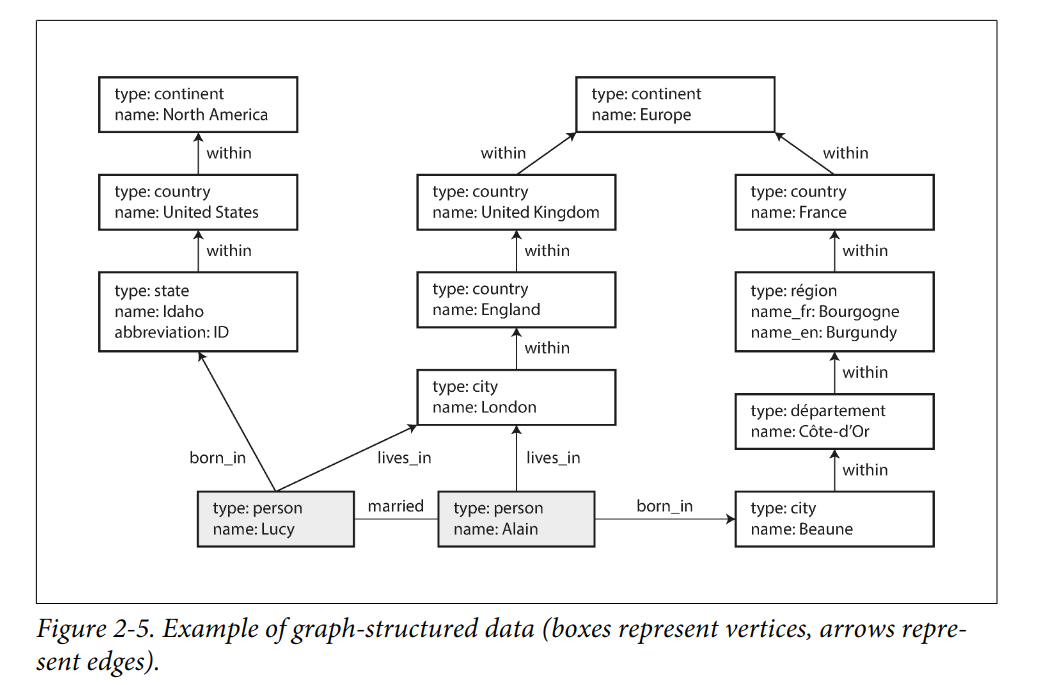
顶点包括:
- 唯一的标识符
- 出边集合
- 入边集合
- 属性集合
边包括:
- 唯一的标识符
- 边的起始点
- 边的终点
- 描述两个顶点之间关系类型的标签
- 属性集合
三元存储
三元存储采取(主体,谓语,客体)的形式存储关系。其中主体相当于图中的起始点,而客体是以下两种情况之一:
- 原始数据类型,比如(lucy,age,33)
- 图中的另一个顶点,即终点。比如(lucy,married,bob)